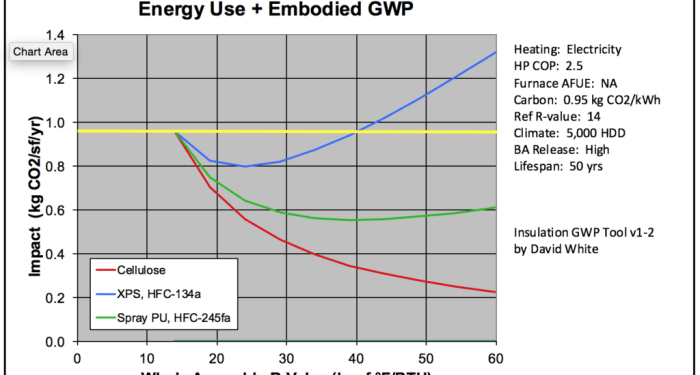
Exploring the profound effects of insulated siding on global energy bills, this introduction sets the stage for a detailed examination of this crucial topic. With a focus on energy efficiency and cost savings, readers will gain valuable insights into the world of insulated siding.
The subsequent paragraph will delve deeper into the types of insulated siding materials and their impact on energy consumption.
Importance of Insulated Siding
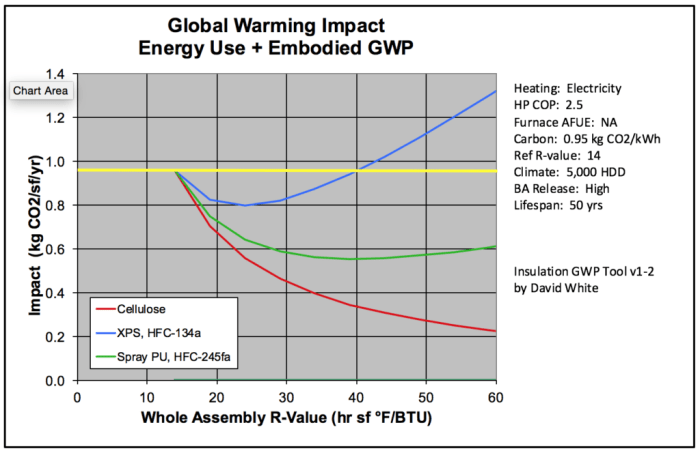
Insulated siding plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency in buildings by providing a barrier against heat loss and reducing energy consumption. This not only helps in maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature but also contributes to significant cost savings on global energy bills.
Impact on Energy Bills
Insulated siding can lead to substantial savings on energy bills as it helps in maintaining a consistent indoor temperature by reducing heat loss. This means that heating and cooling systems do not have to work as hard to regulate the temperature, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs for homeowners.
Reduction in Heat Loss
One of the key benefits of insulated siding is its ability to minimize heat loss through walls. By creating a thermal barrier, insulated siding prevents the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior of a building. This leads to a more stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for continuous heating or cooling and ultimately lowering energy usage.
Energy Consumption
Insulated siding helps in decreasing overall energy consumption by reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems. With improved insulation properties, buildings can maintain a comfortable temperature more efficiently, requiring less energy to keep the indoor environment pleasant. This results in lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint, making insulated siding a sustainable choice for energy-efficient construction.
Types of Insulated Siding
Insulated siding comes in various materials, each offering unique characteristics and benefits. Let’s explore the different types available in the market and how they can help save energy.
Vinyl Insulated Siding
Vinyl insulated siding is a popular choice due to its durability, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness. It provides good insulation, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, vinyl siding is available in a wide range of colors and styles, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of a building.
Foam-backed Insulated Siding
Foam-backed insulated siding consists of a layer of foam insulation attached to the back of the siding panels. This type of siding offers superior thermal performance, effectively reducing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Foam-backed insulated siding also helps in soundproofing and can improve the overall energy efficiency of a property.
Fiber Cement Insulated Siding
Fiber cement insulated siding is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to fire, rot, and pests. It provides excellent thermal insulation, helping to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce heating and cooling costs. Fiber cement insulated siding is also environmentally friendly and can last for many years with minimal maintenance.
Engineered Wood Insulated Siding
Engineered wood insulated siding offers the natural look of wood with enhanced durability and insulation properties. It is available in various textures and finishes, providing a versatile option for homeowners. Engineered wood insulated siding helps in reducing energy bills by keeping the interior comfortable throughout the year while adding a touch of sophistication to the exterior.
Comparing Energy-saving Capabilities
When comparing the energy-saving capabilities of different types of insulated siding, it is essential to consider factors such as R-value, thickness, and installation quality. Foam-backed insulated siding typically offers the highest R-value and thermal performance, followed by fiber cement and engineered wood options.
Vinyl insulated siding also provides significant energy savings compared to traditional siding materials, making it a popular choice for homeowners looking to improve their home’s energy efficiency.
Installation Process
Installing insulated siding is a crucial step in maximizing energy efficiency in a building. Proper installation ensures that the siding performs at its best, providing optimal insulation and reducing energy bills. Here are the steps involved in the installation process and tips for a seamless installation:
Clean and Prepare the Surface
- Remove any existing siding and inspect the walls for damage or rot.
- Repair any issues and ensure the surface is clean and smooth before installation.
Measure and Cut the Siding
- Measure the walls carefully and cut the siding panels to fit.
- Use a saw or specialized cutting tool to ensure precise cuts.
Install the Starter Strip
- Attach a starter strip at the bottom of the wall to provide a base for the siding.
- Ensure the strip is level and securely fastened.
Attach the Siding Panels
- Start at one end of the wall and work your way across, attaching the siding panels according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Use nails or screws to secure the panels in place.
Finish the Corners and Trim
- Install corner pieces and trim around windows and doors to complete the look and seal any gaps.
- Ensure all seams are properly sealed to prevent air leakage.
Final Inspection
- Inspect the entire installation for any gaps, loose panels, or imperfections.
- Make any necessary adjustments to ensure a tight and secure fit.
Global Impact
Insulated siding has the potential to make a significant impact on global energy savings and reducing carbon emissions. By widespread adoption of insulated siding, countries around the world can see a substantial decrease in energy bills and a positive environmental impact.
Energy Savings and Carbon Emissions Reduction
Insulated siding helps to improve the energy efficiency of buildings by reducing heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer. This leads to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling, resulting in decreased energy bills. By reducing the need for constant heating and cooling, insulated siding can contribute to a decrease in carbon emissions on a global scale.
Examples of Impactful Countries/Regions
- United States: In regions with extreme cold or hot climates, such as the Midwest and the South, insulated siding has shown to significantly reduce energy bills for homeowners. This has led to a widespread adoption of insulated siding in these areas.
- Canada: With harsh winters in many parts of the country, insulated siding has become a popular choice for homeowners looking to improve energy efficiency. The use of insulated siding has helped reduce energy consumption and lower heating costs.
- Europe: Countries in Europe, such as Germany and Sweden, have been at the forefront of energy-efficient building practices. Insulated siding is commonly used in these countries to meet strict energy efficiency standards and reduce carbon emissions.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the discussion on the impact of insulated siding on global energy bills highlights the significant role this technology plays in reducing energy costs and carbon emissions. By embracing insulated siding, countries can pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Top FAQs
What are the benefits of insulated siding for energy efficiency?
Insulated siding helps reduce heat loss, leading to lower energy consumption and decreased utility bills.
How does proper installation of insulated siding impact energy efficiency?
Proper installation ensures a tight seal, preventing air leaks and maximizing the insulation’s effectiveness in reducing energy usage.
Can insulated siding really make a significant impact on global energy bills?
Yes, widespread adoption of insulated siding can lead to substantial energy savings on a global scale, benefiting both homeowners and the environment.